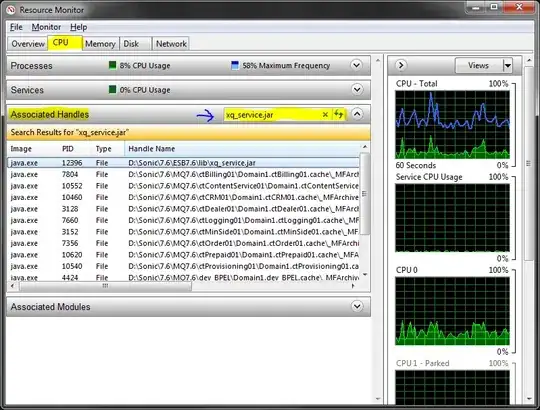
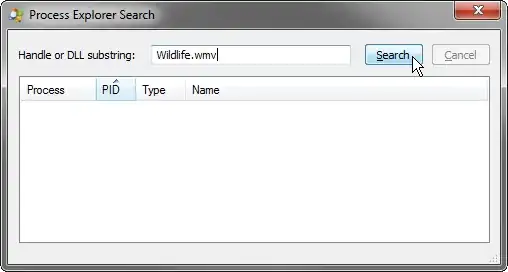
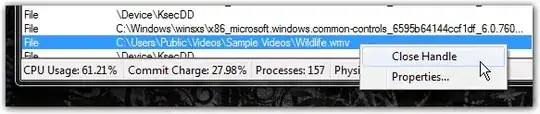
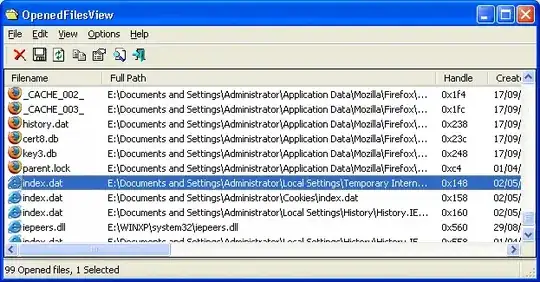
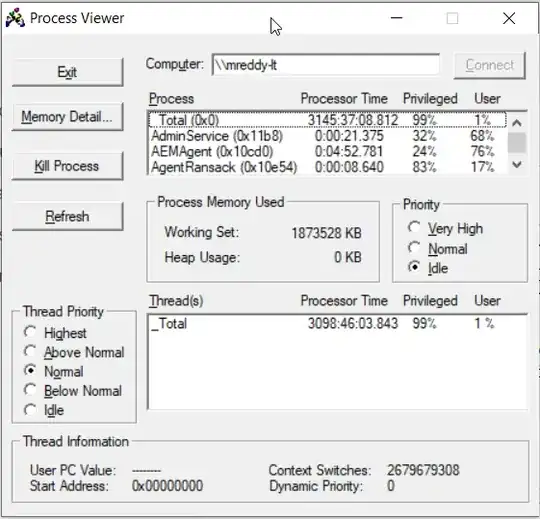
You can also do it programmatically by leveraging on the NTDLL/KERNEL32 Windows API. E.g. have a look at the following code in Python which returns a list of PIDs that can then easily be killed using the Task Manager or similar tools.
import ctypes
from ctypes import wintypes
path = r"C:\temp\test.txt"
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# generic strings and constants
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
ntdll = ctypes.WinDLL('ntdll')
kernel32 = ctypes.WinDLL('kernel32', use_last_error=True)
NTSTATUS = wintypes.LONG
INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE = wintypes.HANDLE(-1).value
FILE_READ_ATTRIBUTES = 0x80
FILE_SHARE_READ = 1
OPEN_EXISTING = 3
FILE_FLAG_BACKUP_SEMANTICS = 0x02000000
FILE_INFORMATION_CLASS = wintypes.ULONG
FileProcessIdsUsingFileInformation = 47
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES = wintypes.LPVOID
ULONG_PTR = wintypes.WPARAM
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# create handle on concerned file with dwDesiredAccess == FILE_READ_ATTRIBUTES
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
kernel32.CreateFileW.restype = wintypes.HANDLE
kernel32.CreateFileW.argtypes = (
wintypes.LPCWSTR, # In lpFileName
wintypes.DWORD, # In dwDesiredAccess
wintypes.DWORD, # In dwShareMode
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES, # In_opt lpSecurityAttributes
wintypes.DWORD, # In dwCreationDisposition
wintypes.DWORD, # In dwFlagsAndAttributes
wintypes.HANDLE) # In_opt hTemplateFile
hFile = kernel32.CreateFileW(
path, FILE_READ_ATTRIBUTES, FILE_SHARE_READ, None, OPEN_EXISTING,
FILE_FLAG_BACKUP_SEMANTICS, None)
if hFile == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE:
raise ctypes.WinError(ctypes.get_last_error())
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# prepare data types for system call
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
class IO_STATUS_BLOCK(ctypes.Structure):
class _STATUS(ctypes.Union):
_fields_ = (('Status', NTSTATUS),
('Pointer', wintypes.LPVOID))
_anonymous_ = '_Status',
_fields_ = (('_Status', _STATUS),
('Information', ULONG_PTR))
iosb = IO_STATUS_BLOCK()
class FILE_PROCESS_IDS_USING_FILE_INFORMATION(ctypes.Structure):
_fields_ = (('NumberOfProcessIdsInList', wintypes.LARGE_INTEGER),
('ProcessIdList', wintypes.LARGE_INTEGER * 64))
info = FILE_PROCESS_IDS_USING_FILE_INFORMATION()
PIO_STATUS_BLOCK = ctypes.POINTER(IO_STATUS_BLOCK)
ntdll.NtQueryInformationFile.restype = NTSTATUS
ntdll.NtQueryInformationFile.argtypes = (
wintypes.HANDLE, # In FileHandle
PIO_STATUS_BLOCK, # Out IoStatusBlock
wintypes.LPVOID, # Out FileInformation
wintypes.ULONG, # In Length
FILE_INFORMATION_CLASS) # In FileInformationClass
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# system call to retrieve list of PIDs currently using the file
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
status = ntdll.NtQueryInformationFile(hFile, ctypes.byref(iosb),
ctypes.byref(info),
ctypes.sizeof(info),
FileProcessIdsUsingFileInformation)
pidList = info.ProcessIdList[0:info.NumberOfProcessIdsInList]
print(pidList)